15 Apr 2019
Golang初识
1. 安装
通过 brew 安装的,所以GOROOT=/usr/local/Cellar/go/1.12.3/libexec/
默认的GOPATH=$HOME/go
2. Go Workspace
它是系统上的一个目录,Go在这个目录下寻找source code文件,管理依赖包,build二进制文件。Go的import语句首先在Go的标准库($GOROOT/src)下寻找,然后是$GOPATH/src。可以有多个Workspace, 只要让GOPATH指向当前workspace即可。
workspace的目录结构必须是:
- src (.go文件)
- pkg (.a文件,可以节约编译时间,
go install command on non-main packages) - bin (
go build <package-name> (main package) or go build program/path.go会在当前目录生成二进制文件,go install command runs go build command internally and output theses files to bin directory)
3. Package
一个标准的可执行Go程序必须有package main声明。
If a program is part of main package, then go install will create a binary file; which upon execution calls main function of the program. If a program is part of package other than main, then a package archive file is created with go install command.
比如src>app>entry.go,里面有main函数,它的package声明是package main,go install app会发生什么呢?
在$GOPATH的src下找到app子目录,编译该包,在bin目录下生成app二进制可执行文件。
go install <package>command looks for any file with main package declaration inside given package directory. If it finds a file, then Go knows this is an executable program and it needs to create a binary file. A package can have many files but only one file with main function, since that file will be entry point of the execution.If a package does not contain file with main package declaration, then Go creates a package archive (.a) file inside pkg directory.
3.1 Export members
An utility package is supposed to provide some variables to a package who imports it. Go exports a variable if a variable name starts with Uppercase.
3.2 Package import
When you import a package, Go creates a global variable using package declaration of the package.
3.3 Nested package
import "greet/de"
3.4 Package initialization
A package scope is a region within a package where a declared variable is accessible from within a package (across all files in the package). This region is the top-most block of any file in the package.
- 在同一个package下声明的包变量(而不是在函数内部),在不同的文件下也能直接使用,即是没有大写字母开头。
- 在同一个package下不允许重新定义同名包变量,但在函数内部是可以的。
- 函数内的变量初始化不允许前面的变量依赖后面定义的变量。
- 包变量可以允许前面的变量依赖后面定义的变量,甚至是定义在同包不同文件中的函数。
3.5 Init function
- 在包被导入的时候即被调用。
- 可以有多个init函数,按照顺序执行
- 在main函数之前执行。
- init函数主要用于初始化全局变量,比如有些变量在package scope没法初始化,如array。
- 同一个package中导入package时该初始化函数只被执行一次(an imported package is initialized only once per package.)
3.6 Package alias
We state a variable name in between import keyword and package name which is new variable to references the package.
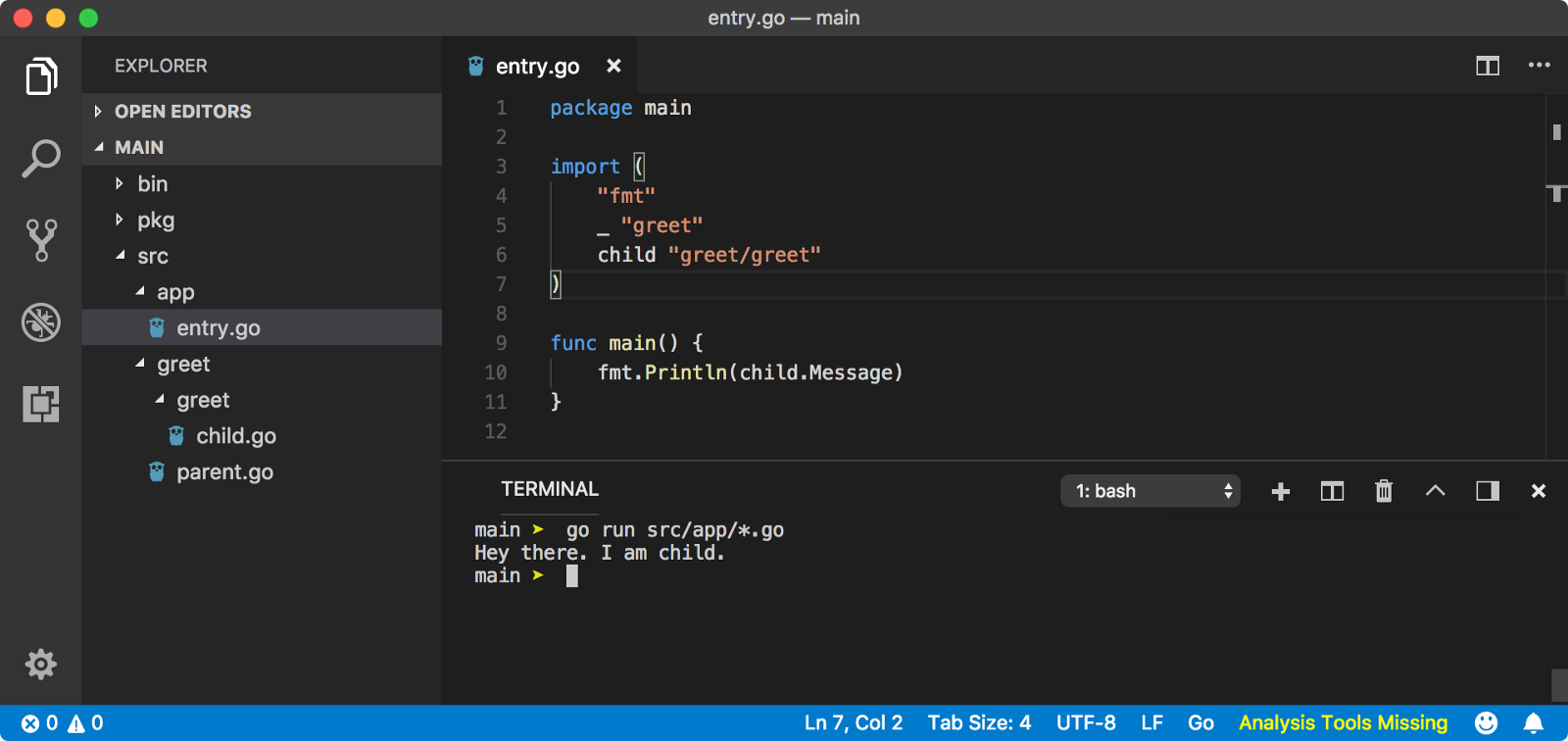
4. 执行顺序
go run *.go
├── Main package is executed
├── All imported packages are initialized
| ├── All imported packages are initialized (recursive definition)
| ├── All global variables are initialized
| └── init functions are called in lexical file name order
└── Main package is initialized
├── All global variables are initialized
└── init functions are called in lexical file name order
5. Variale
- 与其他语言不一样的是,未初始化的变量会被分配相应的zero-value。
- 驼峰命名。
-
类型推导:从已有变量或者初始值复赋值的新变量可以不加类型
var integer1 = 52 //int var string1 = "Hello World" //string var boolean1 = false //bool -
short-hand notation
integer1 := 52 //int string1 := "Hello World" //string boolean1 := false //bool- 只能用于function内部
- 左边至少有一个是新声明的变量
-
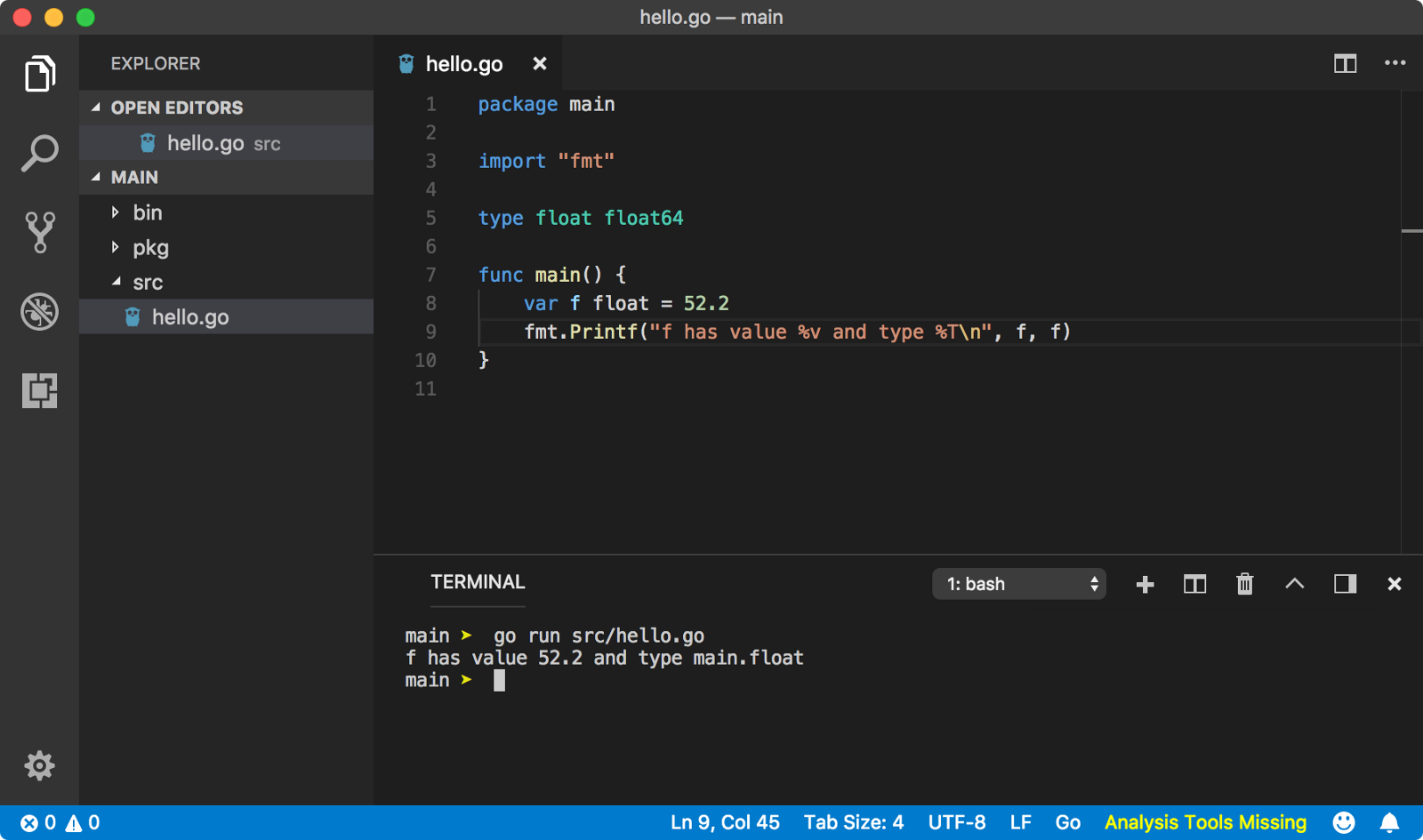
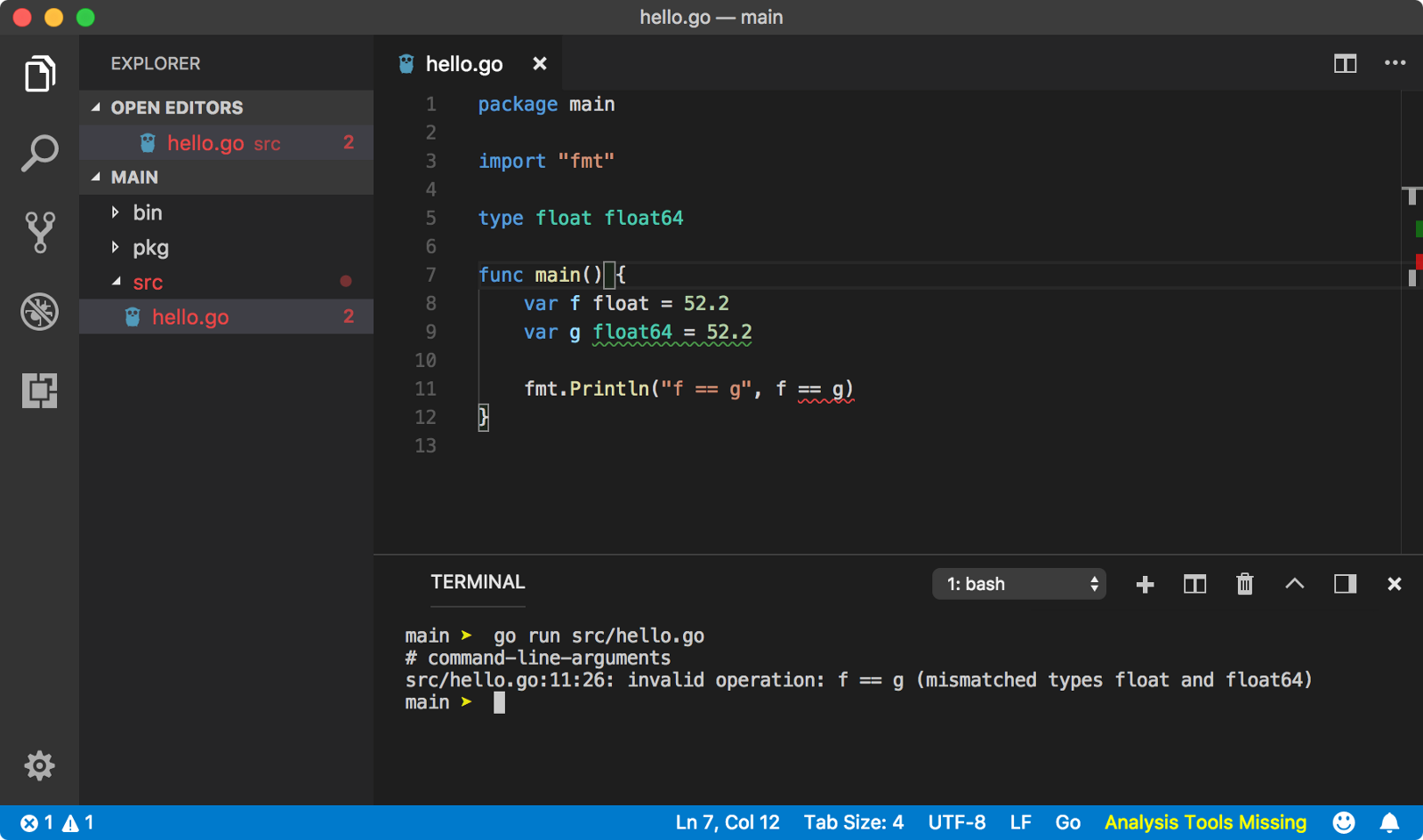
类型转换
var1 := 10 // int var2 := 10.5 // float // illegal // var3 := var1 + var2 // legal var3 := var1 + int(var2) // var3 == 20 -
类型别名
6. Const
const(
a = 1 // a == 1
b = 2 // b == 2
c // c == 2
d // d == 2
)
const(
a = iota // a == 0
b = iota // b == 1
c = iota // c == 2
d // d == 3 (implicitely d = iota)
)
7. Interface
8. Method
method是归属于某种类型的function。它需要额外的一个参数,receiver,定义该method的归属类型。method可以访问receiver的属性。
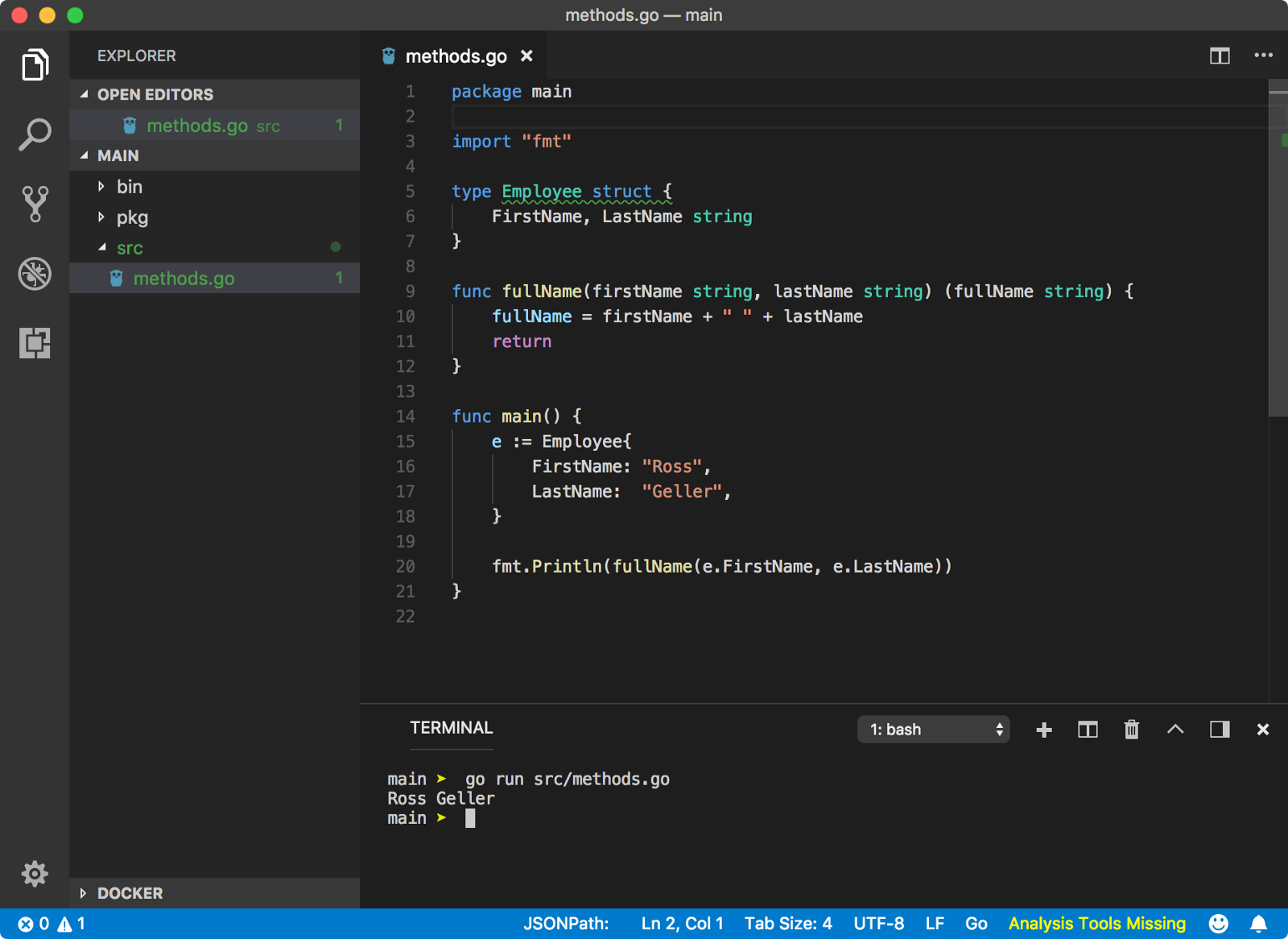
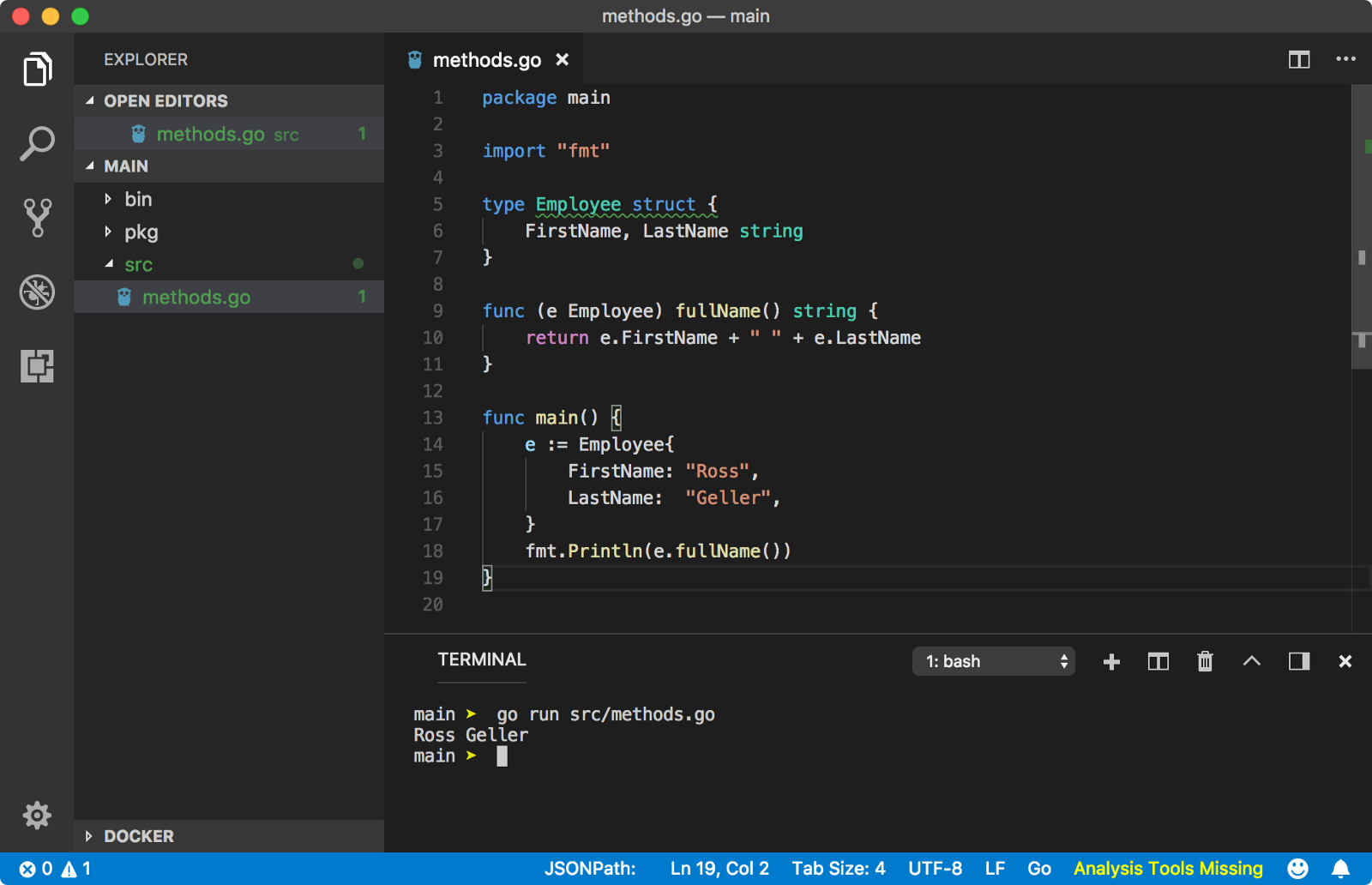
另一个重要的区别是:同一个package下method可以同名(不同类型receiver下相同的方法名),function不能同名。
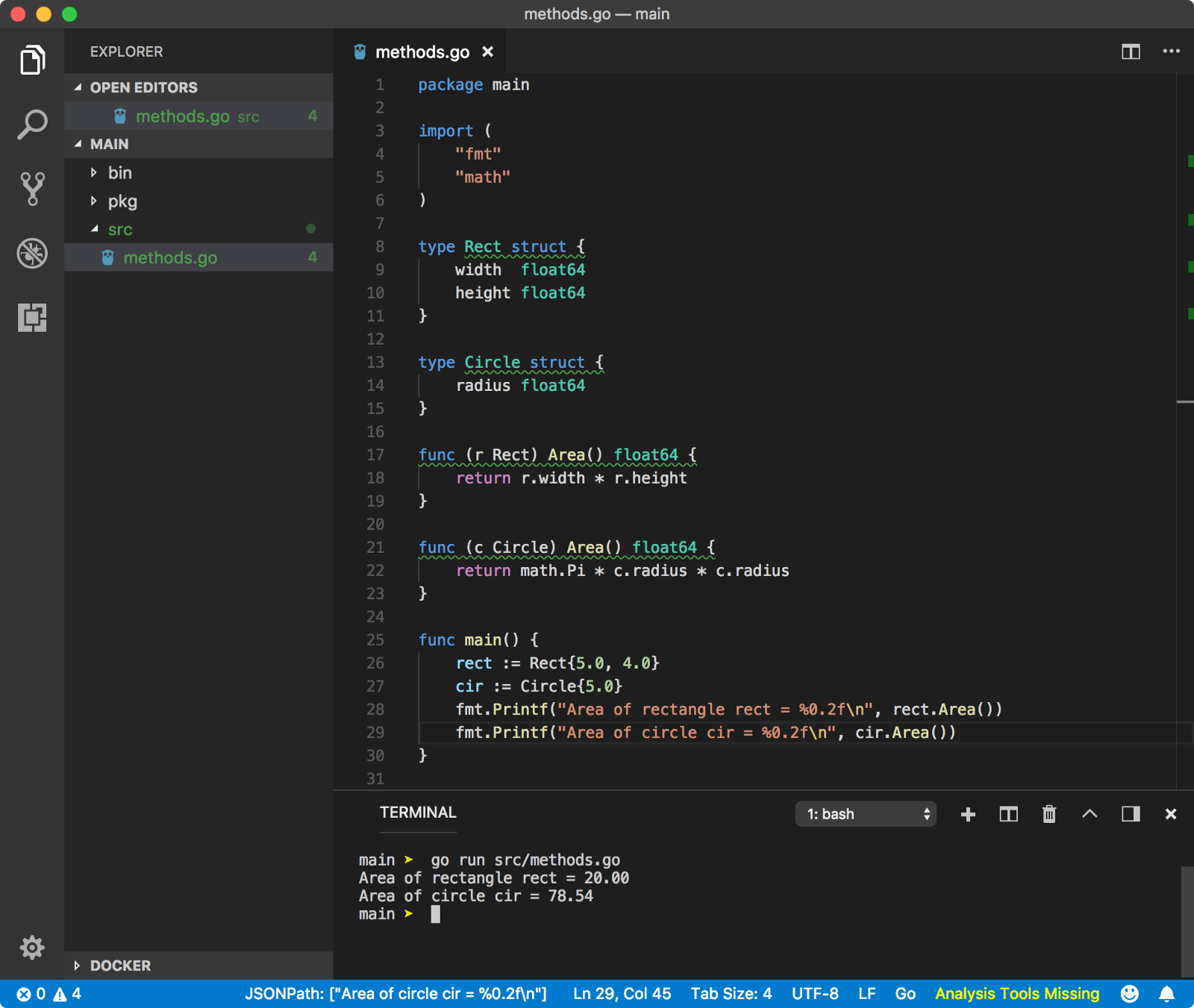
Methods on non-struct type是不允许的。
6.1 Pointer receivers
函数接收的是receiver的备份:
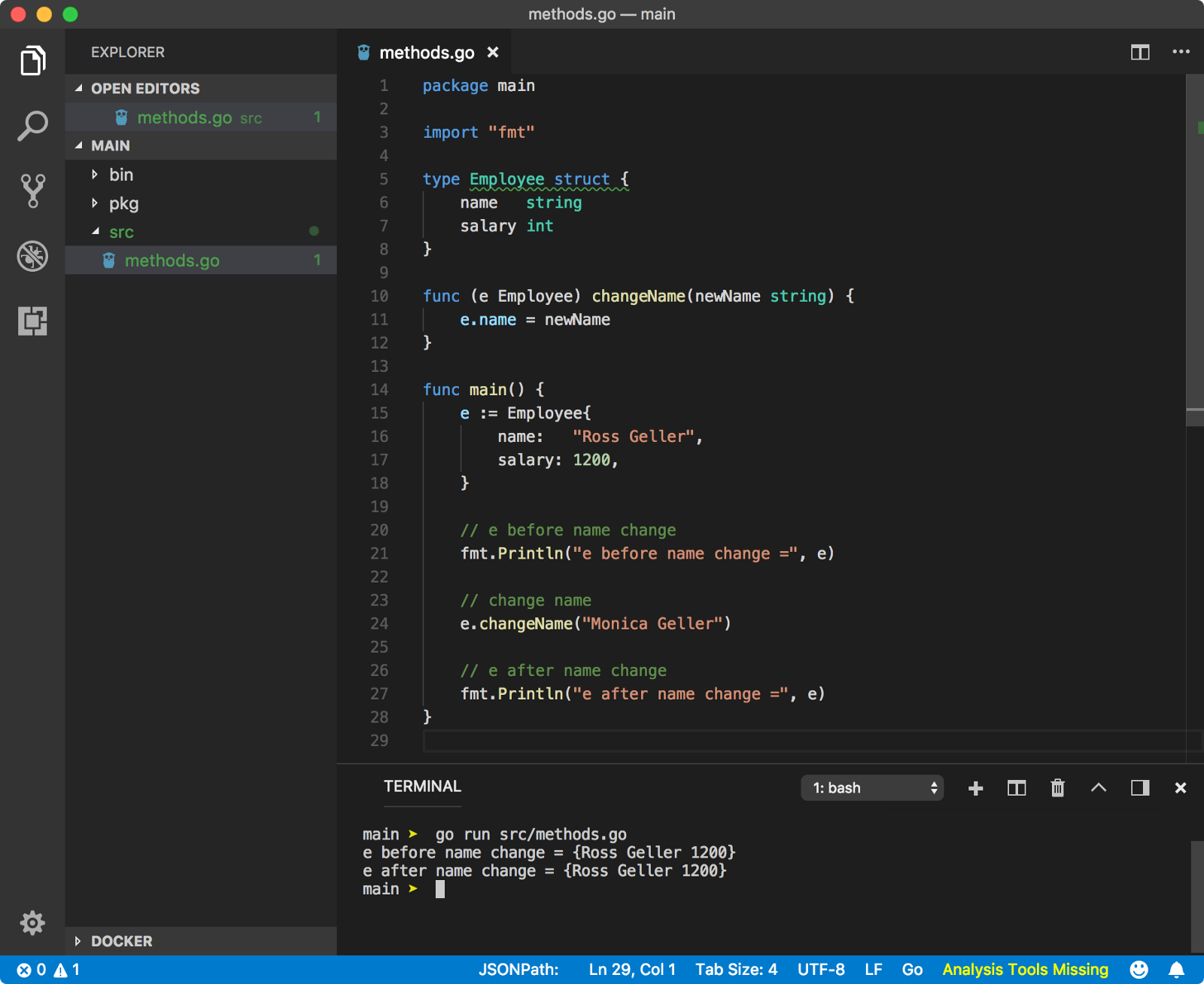
如果想要修改receiver本身,则需要接收receiver指针:
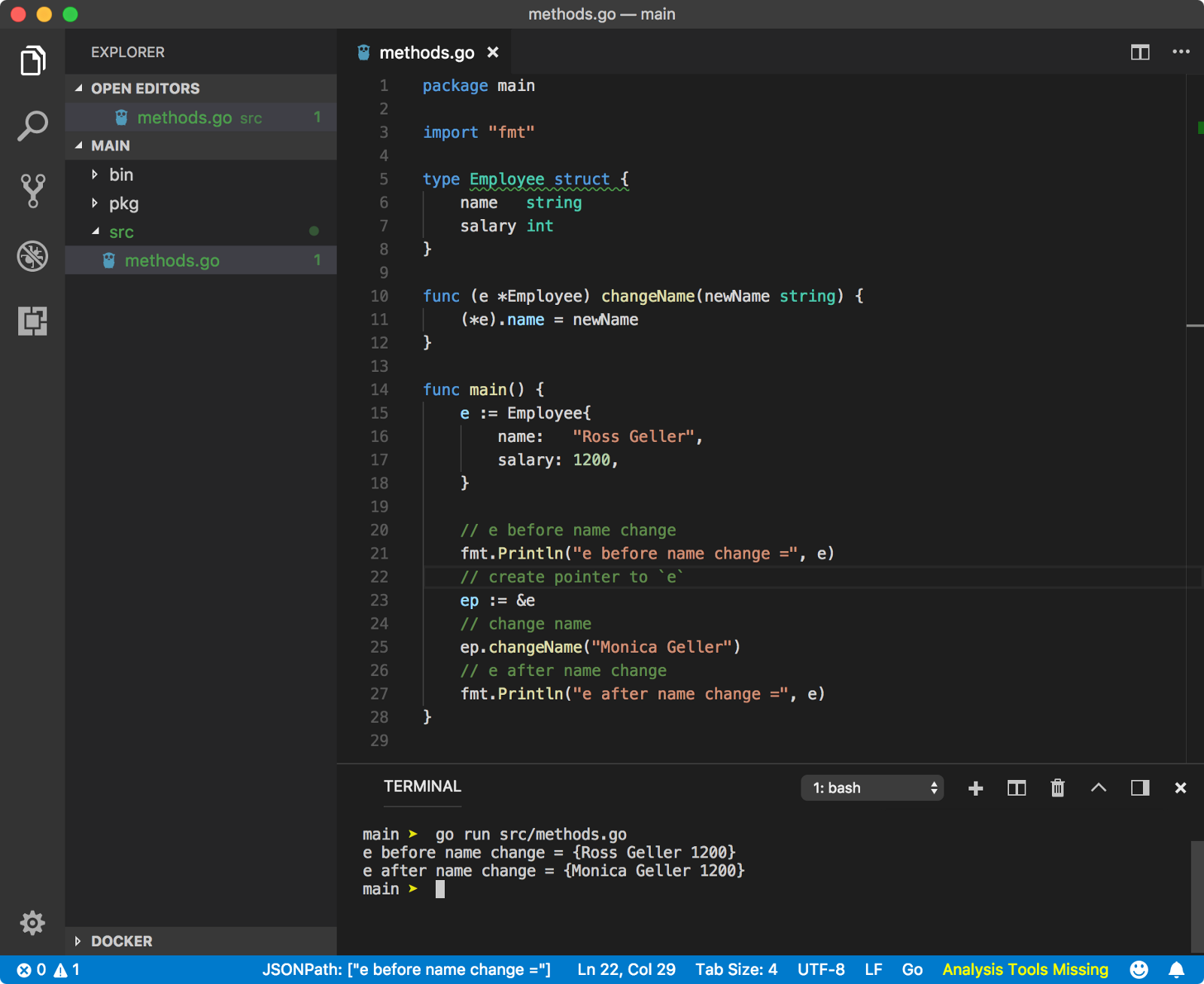
go针对此提供了一些快捷处理:
针对内嵌匿名struct,有prompted field & prompted method.
Method can accept both pointer and value
7. client-go in kubernetes
7.1 client-go对kubernetes资源对象的调用
整个调用的过程如下:
kubeconfig→rest.config→clientset→具体的client(CoreV1Client)→具体的资源对象(pod)→RESTClient→http.Client→HTTP请求的发送及响应
- ClientSet.CoreV1().Pods(“”).List(meta_v1.ListOptions{ LabelSelector: string(nodelabel), })
-
定义变量可以不指定类型吗
-
连接API server
import ( ... "k8s.io/client-go/tools/clientcmd" ) func main() { kubeconfig := filepath.Join( os.Getenv("HOME"), ".kube", "config", ) config, err := clientcmd.BuildConfigFromFlags("", kubeconfig) if err != nil { log.Fatal(err) } ... } -
创建Clientset
func main() { config, err := clientcmd.BuildConfigFromFlags("", kubeconfig) ... clientset, err := kubernetes.NewForConfig(config) if err != nil { log.Fatal(err) } // 获得core API resource api := clientset.CoreV1() }
Til next time,
at 09:42

